
PosteriorMediastinal Masses
PosteriorMediastinal Masses
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Neurogenic Tumors
Peripheral nerve origin
Neurofibromas
Neurilemomas (Schwannomas)

Neurogenic Tumors
Sympathetic nerve origin
GanglioneuromasUsually benign
NeuroblastomasUsually malignant
SympathicoblastomasUsually malignant
Paraganglionic cells
Pheochromocytoma
Chemodactomas (paragangliomas)—benign ormalignant

Posterior MediastinumAnatomy
Bordered anteriorly by pericardium
Posteriorly by anterior border of spine
Paravertebral gutters technically excluded fromposterior mediastinum
For practical purposes considered part of it

Posterior MediastinumContents
Descending aorta
Esophagus
Thoracic duct
Vagus nerves
Nodes

Posterior Mediastinal MassesBenign vs. Malignant
About 30% malignant
Nerve sheath tumors most common andusually benign
Neoplasms which arise from nerveelements other than sheath usuallymalignant

Posterior Mediastinal MassesNeurofibromas
In adults, neurofibroma and neurilemomas(Schwannomas) most common
Neurofibroma contains Schwann cells plusnerve cells
Occur 3rd or 4th decade
Schwannoma derived from sheath of Schwannwithout nerve cell

Posterior Mediastinal MassesGanglioneuroma
In children, ganglioneuroma andneuroblastoma are most common
Ganglioneuromabenign tumor
Neuroblastomamalignant tumor

Posterior Mediastinal MassesNeuroblastoma
Very malignant, undifferentiated roundcell lesion
From sympathetic ganglion
Usually <10 years old
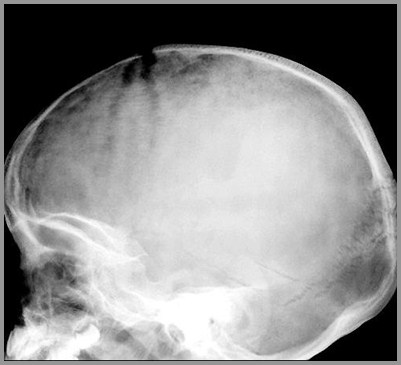
Produces “iron-filings” appearance tosutures in skull infiltrated with tumor

“Iron Filings” appearance of suture from metastases from neuroblastoma
“Iron Filings” appearance of suture from metastases from neuroblastoma

Posterior Mediastinal MassesCalcification
Calcification in posterior mediastinalmass points to neural tumor in childrather than met from somewhere else

Posterior Mediastinal MassesGeneral
Posterior mediastinal neurofibromasonly rarely associated withneurofibromatosis
Most have no symptoms

Posterior Mediastinal MassesImaging
Rib erosions
Both benign and malignant
Enlarged neural foramina (dumbell shapedlesion)
Scalloping of posterior vertebral bodies
Scoliosis
Pleural effusion
Both benign and malignant neural tumor

NeurofibromaMultiple subcutaneous neurofibromas (yellow arrows)
NeurofibromaMultiple subcutaneous neurofibromas (yellow arrows)
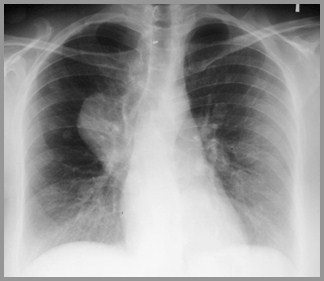
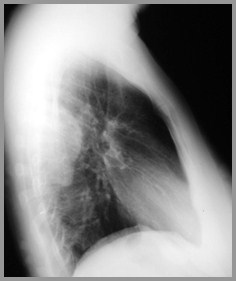

Posterior Scalloping of lumbarvertebral bodies in neurofibromatosis
Posterior Scalloping of lumbarvertebral bodies in neurofibromatosis
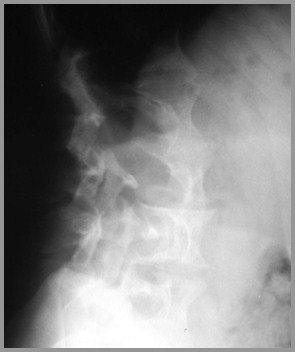

Lateral Meningocele in neurofibromatosis
Lateral Meningocele in neurofibromatosis
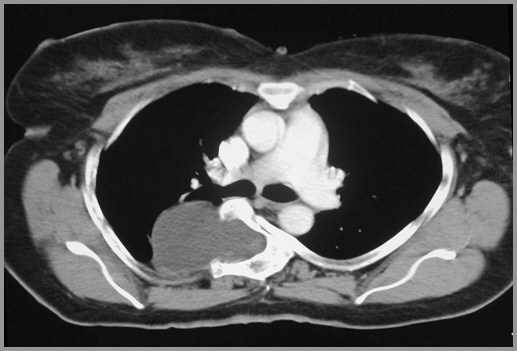

Posterior Mediastinal MassesParaspinal Abscess
Paraspinal abscess from TB – look fordestruction of two contiguous endplatesplus narrowing of intervening disc space

Posterior Mediastinal MassesOther Causes
Neurenteric cysts may have associatedhemivertebra
Extramedullary hematopoiesis should beassociated with splenomegaly andsometimes widening of ribs

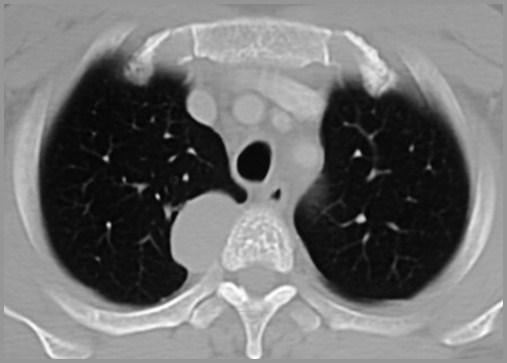
Posterior mediastinal mass from extramedullary hematopoiesis
Posterior mediastinal mass from extramedullary hematopoiesis

The End
The End